GSH 138-01-94: An old supernova remnant in the far outer Galaxy
Stil, J.M. & Irwin, J.A. (2001), "GSH 138-01-94: An old supernova remnant in the far outer Galaxy",
ApJ, 563, 816
We present the peculiar expanding HI shell GSH 138-01-94, discovered in the
Canadian Galactic Plane Survey (recently expanded into the International
Galactic Plane Survey). This shell is unique because of its unusual location,
in the outermost regions of the Galactic disk. The properties of the shell
are discussed, as well as possible origins. This leads to the interpreattion
that GSH 138-01-94 is probably the remnant of a supernova explosion that
occurred 4.3 million years ago in the outer Galaxy. As such, GSH 138-01-94
is the largest, oldest supernova remnant known to date. We relate the
peculiar properties of this objects to the special environment in which it
was found.
The complete paper is available as electronic preprint
astro-ph/0108368
gzipped postscript
Press Release
The Canadian
Galactic Plane Survey allows a multi-wavelength view of the Galaxy
in unprecedented detail. One of the beautiful structures found in the
survey data is the expanding shell of hydrogen gas GSH 138-01-94. The
name of the shell contains the Galactic coordinates according to guide
lines set by the IAU.
GSH 138-01-94 is a very large shell: diameter 360 parsec, more than
1000 lightyears. At this time, the shell is still expanding
with a velocity of 11.8 km/s.
More about GSH 138-01-94 on the CASCA 2001 poster

Click on details of the image to learn more
Image prepared by Jayanne English
|
This is a multi-wavelength image of GSH 138-01-94.
Colour shades
represent observations at different frequencies. Click on a detail
in the image to read more about it.
The image shows the shell of atomic hydrogen, radio continuum sources,
a molecular cloud, and infrared emission from interstellar dust.
Animation of the 21-cm line data (JAVA)
|
|
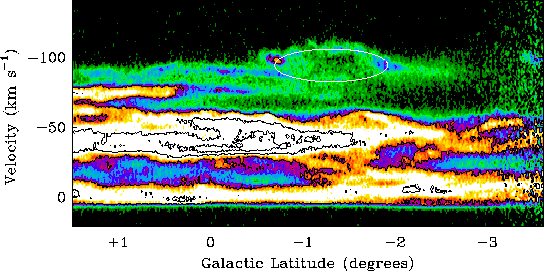
This image shows
the distribution of atomic hydrogen gas in velocity in a plane
perpendicular to the Galactic equator. The white ellipse represents a
model described in the paper, that best
describes the expansion of the shell. In general, there is no emission
with a velocity beyond (-100 km/s). This "limit" represents the outer
edge of the Galactic HI disk. Only emission related to the shell is
seen at more extreme velocities.
Links


